Product Description
Product Description
Customized Metal injection molding MIM powder metallurgy products
| Product Name | Powder Metallurgy Products |
| Material | Iron Powder ( Fe, Cu, C, Sn, Zn, Pb etc), Copper Powder, Stainless Steel Powder |
| Density Range | 6.0-7.1 g/cm3 |
| Standard | DIN GB ISO JIS BA ANSI |
| Material Grade | FC 5715, FC 5718, FC0505, FC 0508, FC0808 |
| Processing | Mix Powder-Processing-Sintering-Shaping-Surface Treatment-Packing-Delivery |
| Surface Treatment | Grinding, Machining, Oil Immersion, Steam Oxidation, Electroplate |
| Appication | Automobile Parts, Motorcycle Parts, Electrical Tools Parts, Home Appliance Part |
FAQ
-
How to contact with your company?
Please make call to to send me the drawings and details.
-
What does your company need to submit a quotation?
Drawing or sample, together with relevant information, such as quantity, weight, material,
-
Which kind of format of the drawing?
PDF, IGS, DWG, STEP, etc
-
What if we do not have a drawing?
We can duplicate your sample and make drawing for your confirmation.
-
How soon before I get a sample?
4 weeks for mold and sample, 3 days for express.
-
Where does your company locate?
HangZhou, China, which is famous of HangZhou Beer and Metal Parts.
-
Can I visit your company?
Yes, sure, welcome your visit anytime. We will book hotel and pick you up from airport.
| Certification: | TS16949, ISO9001 |
|---|---|
| Binder Type: | Acrylic Binder |
| Powder Type: | MIM |
| Transport Package: | Customized |
| Specification: | Customized |
| Trademark: | OEM |
| Samples: |
US$ 0/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | |
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
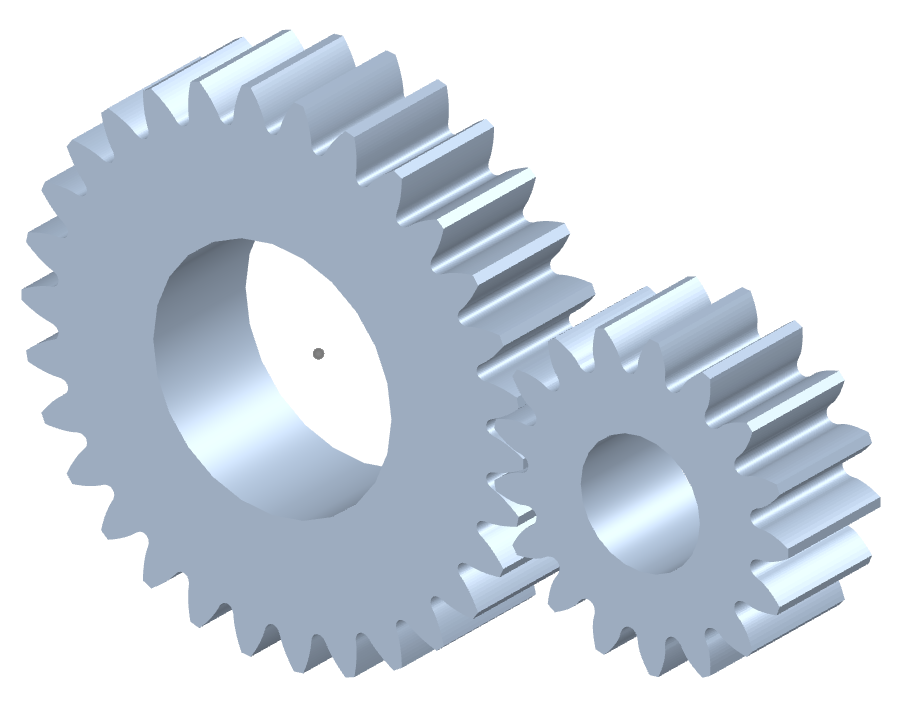
How do you ensure proper alignment when connecting spur gears?
Proper alignment is crucial when connecting spur gears to ensure smooth and efficient gear operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to ensure proper alignment when connecting spur gears:
- Visual Inspection: Start by visually inspecting the gears, gear shafts, and associated components for any visible misalignment or damage. Look for signs of wear, uneven tooth engagement, or any abnormalities that may affect alignment.
- Shaft Alignment: Align the gear shafts accurately before connecting the gears. Proper shaft alignment ensures that the gears are positioned correctly relative to each other. This can be achieved through various alignment techniques, such as using alignment tools, laser alignment systems, or measuring devices. The goal is to ensure parallel or coaxial alignment between the gear shafts.
- Backlash Adjustment: Adjust the backlash between the gear teeth to achieve proper alignment. Backlash refers to the slight gap between the mating teeth of gears. It is important to maintain an appropriate amount of backlash to allow for smooth gear engagement and minimize the risk of binding or jamming. Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations or industry standards for the recommended backlash range and adjust as necessary during gear installation.
- Check Gear Mesh: Verify the gear meshing pattern to ensure proper alignment. The gear teeth should mesh smoothly and evenly without any signs of excessive or uneven contact. If there are indications of improper meshing, such as concentrated contact on a specific area of the tooth, it may imply misalignment or other issues that need to be addressed.
- Shim Adjustment: If misalignment is detected, shimming can be employed to correct it. Shimming involves placing thin metal shims between the gear and the shaft to adjust the positioning and alignment. Shims are available in various thicknesses, allowing for precise alignment adjustments. Careful measurement and selection of the appropriate shim thickness can help achieve the desired alignment.
- Tightening Bolts: When connecting the gears to the shafts, ensure that the bolts or fasteners are tightened evenly and to the recommended torque specifications. Uneven tightening can introduce misalignment or uneven load distribution, leading to gear misalignment and potential issues.
- Post-Installation Verification: After connecting the gears, perform a final verification of the alignment. Rotate the gears manually or through the gear system’s intended operation and observe the gear meshing behavior. Look for any signs of abnormal noise, vibration, or irregular tooth engagement. If any issues are detected, further adjustments or inspections may be necessary.
- Regular Maintenance: Implement a proactive maintenance program that includes periodic inspections and alignment verification. Gears can experience wear or misalignment over time due to factors such as load variations, temperature changes, or prolonged operation. Regular maintenance allows for early detection and correction of alignment issues, ensuring optimal gear performance and longevity.
Proper alignment is essential for maximizing the efficiency, durability, and reliability of spur gear systems. By following these alignment practices and considering the manufacturer’s recommendations, industry standards, and expert advice, you can ensure proper alignment when connecting spur gears.
It’s important to note that the specific alignment techniques and procedures may vary depending on the gear system’s design, size, application, and other factors. Consulting with gear manufacturers, engineers, or alignment specialists can provide further guidance on the recommended alignment practices for your specific gear system.
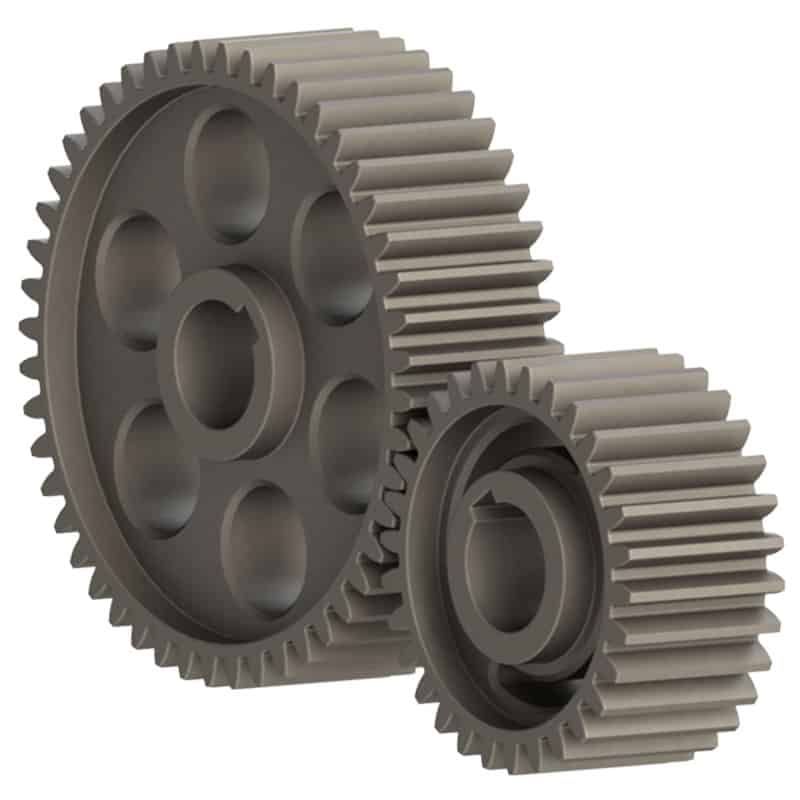

How do you install a spur gear system?
Installing a spur gear system involves several steps to ensure proper alignment, engagement, and operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how to install a spur gear system:
- Preparation: Before installation, gather all the necessary components, including the spur gears, shafts, bearings, and any additional mounting hardware. Ensure that the gear system components are clean and free from debris or damage.
- Shaft Alignment: Proper shaft alignment is crucial for the smooth operation of a spur gear system. Ensure that the shafts on which the gears will be mounted are aligned accurately and parallel to each other. This can be achieved using alignment tools such as dial indicators or laser alignment systems. Adjust the shaft positions as needed to achieve the desired alignment.
- Positioning the Gears: Place the spur gears on the respective shafts in the desired configuration. Ensure that the gears are positioned securely and centered on the shafts. For shafts with keyways, align the gears with the key and ensure a proper fit. Use any necessary mounting hardware, such as set screws or retaining rings, to secure the gears in place.
- Checking Gear Engagement: Verify that the teeth of the gears mesh properly with each other. The gear teeth should align accurately and smoothly without any excessive gaps or interference. Rotate the gears by hand to ensure smooth and consistent meshing throughout their rotation. If any misalignment or interference is observed, adjust the gear positions or shaft alignment accordingly.
- Bearing Installation: If the spur gear system requires bearings to support the shafts, install the bearings onto the shafts. Ensure that the bearings are the correct size and type for the application. Press or slide the bearings onto the shafts until they are seated securely against any shoulder or bearing housing. Use appropriate methods and tools to prevent damage to the bearings during installation.
- Lubrication: Apply a suitable lubricant to the gear teeth and bearings to ensure smooth operation and reduce friction. Refer to the gear manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate lubrication type and amount. Proper lubrication helps minimize wear, noise, and heat generation in the gear system.
- Final Inspection: Once the gears, shafts, and bearings are installed, perform a final inspection of the entire spur gear system. Check for any unusual noises, misalignment, or binding during manual rotation. Verify that the gears are securely mounted, shafts are properly aligned, and all fasteners are tightened to the specified torque values.
It’s important to follow the specific installation instructions provided by the gear manufacturer to ensure proper installation and operation. Additionally, consult any applicable industry standards and guidelines for gear system installation.
By carefully following these installation steps, you can ensure a well-aligned and properly functioning spur gear system in your machinery or equipment.

Can you explain the concept of straight-cut teeth in spur gears?
The concept of straight-cut teeth is fundamental to understanding the design and operation of spur gears. Straight-cut teeth, also known as straight teeth or parallel teeth, refer to the shape and arrangement of the teeth on a spur gear. Here’s a detailed explanation of the concept of straight-cut teeth in spur gears:
Spur gears have teeth that are cut straight and parallel to the gear axis. Each tooth has a uniform width and thickness, and the tooth profile is a straight line. The teeth are evenly spaced around the circumference of the gear, allowing them to mesh with other spur gears.
The key characteristics and concepts related to straight-cut teeth in spur gears include:
- Tooth Profile: The tooth profile of a spur gear with straight-cut teeth is a straight line that extends radially from the gear’s pitch circle. The profile is perpendicular to the gear axis and remains constant throughout the tooth’s height.
- Pitch Circle: The pitch circle is an imaginary circle that represents the theoretical point of contact between two meshing gears. For a spur gear, the pitch circle is located midway between the gear’s base circle (the bottom of the tooth profile) and the gear’s addendum circle (the top of the tooth profile).
- Pressure Angle: The pressure angle is the angle between the line tangent to the tooth profile at the pitch point and a line perpendicular to the gear axis. It determines the force distribution between the meshing teeth and affects the gear’s load-bearing capacity and efficiency. Common pressure angles for spur gears are 20 degrees and 14.5 degrees.
- Meshing: Straight-cut teeth in spur gears mesh directly with each other. The teeth engage and disengage along a line contact, creating a point or line contact between the contacting surfaces. This direct meshing arrangement allows for efficient power transmission and motion transfer.
- Advantages and Limitations: Straight-cut teeth offer several advantages in spur gears. They are relatively simple to manufacture, resulting in cost-effective production. Moreover, they provide efficient power transmission and are suitable for moderate to high-speed applications. However, straight-cut teeth can generate more noise and vibration compared to certain other tooth profiles, and they may experience higher stress concentrations under heavy loads.
In summary, straight-cut teeth in spur gears refer to the straight and parallel arrangement of the gear’s teeth. The teeth have a uniform profile with a constant width and thickness. Understanding the concept of straight-cut teeth is essential for designing and analyzing spur gears, considering factors such as tooth profile, pitch circle, pressure angle, meshing characteristics, and the trade-offs between simplicity, efficiency, and noise considerations.


editor by CX 2023-09-04